class GraphMatrix { char[] vertices; // 노드 int[][] matrix; // 인접 행렬 int idx; public GraphMatrix(int size) { this.vertices = new char[size]; this.matrix = new int[size][size]; this.idx = 0; } public boolean isFull(){ return this.vertices.length == idx; } public void addVertex(char c) { if(isFull()){ System.out.println("Graph is full"); return; } this.vertices[this.idx++] = c; } public void addEdg..
자료구조
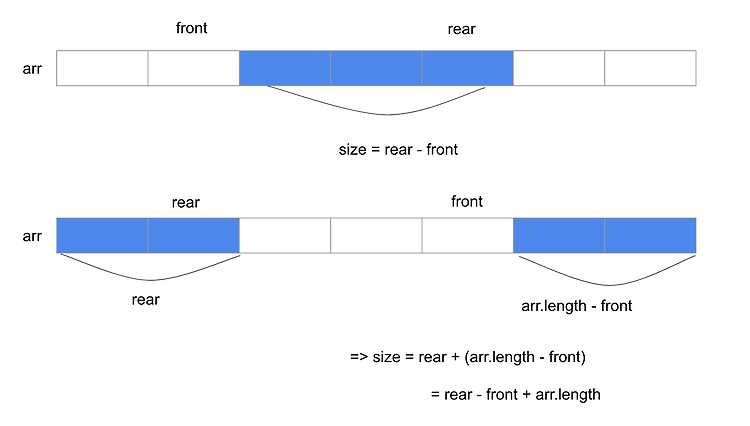
이번 게시물은 제가 좋아하는 유튜버(간다효)처럼 제목을 지어봤습니다. 원형큐에서 큐의 길이를 구할 때는 두가지 경우로 나눠서 생각해봐야 합니다. 1. front가 앞에, rear가 뒤에 있는 상황 2. rear가 앞에, front가 뒤에 있는 상황 소스코드로 나타내면 이렇게 볼 수 있는데요, int size; if (rear - front < 0) { size = rear - front + arr.length; } else { size = rear - front; } 공식처럼 생각하면 그렇구나, 하고 넘어갈 수 있지만 .. 머리속으로 떠올리면 또 쉽게 이해가 되지 않아서.. 직접 그려보았습니다.. rear - front가 음수일 경우는 rear가 배열의 앞쪽에, front가 배열의 뒷쪽에 위치한 상태로 ..
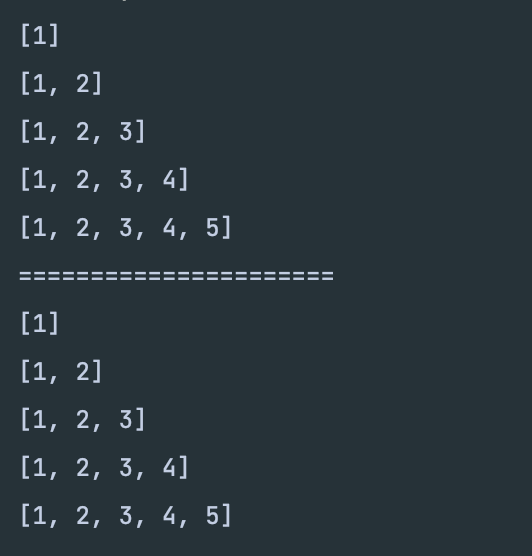
알고리즘 문제를 풀다가 헷갈리는 상황이 생겼습니다.. 링크드 리스트, 큐, 데크 등의 선형 자료구조의 이미지를 떠올릴 때.. 어디가 앞이고 어디가 뒤인 거지? (front) LIST (last) //..? 혹은 (last) LIST (front) // 어디가 front야..? 위 상황에서 보통 add()와 addLast()라는 메소드가 있으니까.. 두 메소드는 반대의 기능을 하는걸까...? add-->> (front) LIST (last) (front) LIST (last) (last) LIST (front) (last) LIST (front) (front) LIST (rear) (front) LIST (rear) 4 [1, 2, 3] deque.removeFirst() ==> 1 [2, 3] deque..